|
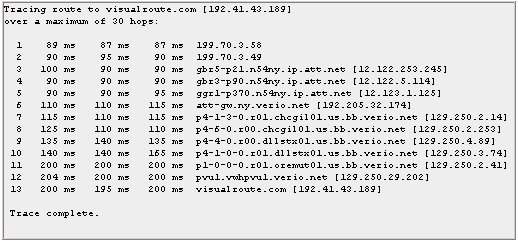
Tracert (and ping) are both command line utilities that are built into
Windows and most other computer systems. The basic tracert command
syntax is "tracert hostname". For example, "tracert visualroute.com" and
the output might look like:
Tracert(ping)都是windows系统和其它多数电脑系统内置的命令行工具。基本的tracert命令语法是:“tracert
hostname”。例如,“tracert visualroute.com”,输出如下图:
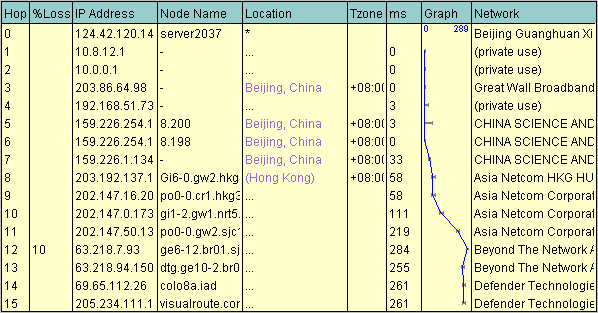
Here is a similar trace route as it would appear in a VisualRoute table:
以下是VisualRoute输出一个类似的路由跟踪表格:
Discover the path: Tracert sends an ICMP echo packet, but it takes
advantage of the fact that most Internet routers will send back an ICMP
'TTL expired in transit' message if the TTL field is ever decremented to
zero by a router. Using this knowledge, we can discover the path taken
by IP Packets.
路由发现:Tracert发送一个ICMP报文,当一个路由器发现TTL域的值减到0时会回传一个“TTL过期”的消息。利用这一点,我们可以利用IP报文来发现路由。
How tracert works:Tracert sends out an ICMP echo packet to the named
host, but with a TTL of 1; then with a TTL of 2; then with a TTL of 3
and so on. Tracert will then get 'TTL expired in transit' message back
from routers until the desination host computer finally is reached and
it responds with the standard ICMP 'echo reply' packet.
Tracert如何工作:Tracert发送一个目的为要测试主机的ICMP报文,但是TTL设为1;然后发一个TTL为2;接着发一个TTL为3依此类推。Tracert将从到目的地中间的各个路由器上收到“TTL过期”消息,最后到达目的服务器并收到正常的“回声响应”消息。
Try it yourself: To see this in action yourself, just use the '-i'
option of ping, which allows you to set the TTL value of outgoing ping
packets. For example, "ping -i 1 visualroute.com" and you will see
"Reply from 199.70.3.58: TTL expired in transit" (where the router IP
Address returned, 199.70.3.58, is specific to your Internet connection).
Then again with "ping -i 2 visualroute.com", and get back "Reply from
199.70.3.49: TTL expired in transit", and so on. Finally at "ping -i 13
visualroute.com" you get "Reply from 192.41.43.189: bytes=32 time=198ms
TTL=245", which is the destination host responding.
自己试试:要自己测试这个功能,可以使用ping命令的'-i'参数,这个参数允许您在发出的ping包中设置TTL值。例如,"ping -i 1
visualroute.com",您将会看到"Reply from 199.70.3.58: TTL expired in
transit"的响应(其中路由器返回的IP地址199.70.3.58和您的网络有关,这里只是举例)。然后,您再用命令“ping -i 2
visualroute.com”,可以看到返回“Reply from 199.70.3.49: TTL expired in
transit”,依此类推,直到使用“ping -i 13 visualroute.com”命令时得到返回“"Reply from
192.41.43.189: bytes=32 time=198ms TTL=245”,这个是目的主机的响应。
Round Trip Times: Each millisecond (ms) time in the table is the
round-trip time that it took (to send the ICMP packet and to get the
ICMP reply packet). The faster (smaller) the times the better. ms times
of 0 mean that the reply was faster than the computers timer of 10
milliseconds, so the time is actually somewhere between 0 and 10
milliseconds.
响应时间:表中的ms(毫秒)栏是获得的响应时间。(从发出ICMP报文到收到ICMP响应之间的时间差)。值越小越好。Ms的时间为0表示响应速度比计算机的定时器10毫秒还要快。实际时间在0到10毫秒之间。
Packet Loss: Packet loss kills throughput. So, having no packet loss is
critical to having a connection to the Internet to responds well. A
slower connection with zero packet loss can easily outperform a faster
connection with some packet loss. Also, packet loss on the last hop, the desination, is what is most important. Sometimes routers in-between will
not send ICMP "TTL expired in transit" messages, causing what looks to
be high packet loss at a particular hop, but all it means is that the
particular router is not responding to ICMP echo.
丢包:丢包导致网络中断,因此,没有丢包对于Internet连接至关重要。一个慢速的没有丢包的网络连接要优于一个快速的但是存在丢包的连接。最后一跳也就是目的主机的是否丢包是最重要的。有时,一些中间路由器不会发出ICMP的"TTL
expired in transit"消息,看起来像是某个特定节点存在高丢包率,实际上只是表明这个特定的路由器不对ICMP报文作出响应。
TOP |